Featured
What Happens To The Temperature During A Phase Change
What Happens To The Temperature During A Phase Change. In the case of freezing, energy is subtracted as the molecules bond to one another. However, the graph levels out.
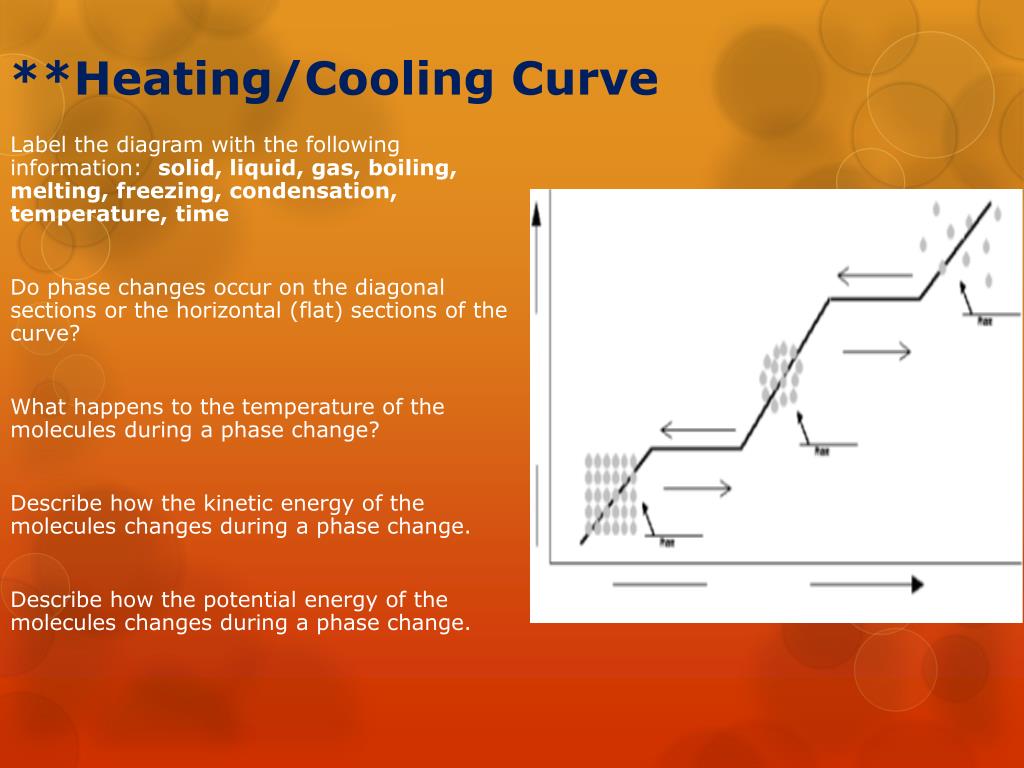
If you graph the heat added to a system versus the system’s temperature, the graph usually slopes upward; These energy exchanges are not changes in kinetic energy. The temperature of a substance does not change as the substance goes from one phase to another.
In The Case Of Freezing, Energy Is Subtracted As The Molecules Bond To One Another.
This says that a sublimation phase change could happen, for example, at a constant 1 atm by increasing the temperature past about −78.5∘c. The emitted heat causes the temperature of the ice cubes to rise at first. What happens to the temperature of a substance during a phase change?
It Stays The Same As Energy Is Added.
During a phase change, the temperature remains the same until the phase. When a substance undergoes a first order phase change, its temperature remains constant as long as the phase change remains incomplete. No part of it is used.
Or The Temperature Of A Substance Does Not Change During A.
Phase change involves the transition of substances from one. These changes occur when sufficient energy is supplied to the system (or a. The temperature of a substance remains the same during phase change.
During A Phase Change, The Temperature Remains Constant Until The Phase Change Is Complete.
The temperature of a substance does not change as the substance goes from one phase to another. During phase change, the energy supplied is used only to separate the molecules ; It stays the same as energy is added.
You Have To Give To (Or Take From) The System.
But there is no temperature change until a phase change is complete. They are changes in bonding. During phase change, the energy supplied is used only to.
Popular Posts
Change Image From Rgb To Cmyk Indesign
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Comments
Post a Comment